Adds a 3D representation of trees to an existing 3D scene generated with rayshader.
Users can specify the trees' geographical positions using latitude and longitude or the same coordinate reference system as extent.
Different types of tree models can be used, including a basic and a cone-shaped tree. Users can also use their own custom tree model in
OBJ format. The function allows customization of various aspects of the tree, including the color of the crown and the trunk,
the size of the crown (the leafy part of the tree) and the trunk, the overall scale of the tree, and the rotation angle around the x, y, and z axes.
Users can also specify the minimum and maximum height of the trees to be rendered.
render_tree(
lat = NULL,
long = NULL,
extent = NULL,
type = "basic",
custom_obj_tree = NULL,
custom_obj_crown = NULL,
custom_obj_trunk = NULL,
crown_color = "#22aa22",
trunk_color = "#964B00",
absolute_height = FALSE,
tree_height = NULL,
trunk_height_ratio = NULL,
crown_width_ratio = NULL,
crown_width = NULL,
trunk_radius = NULL,
tree_zscale = TRUE,
min_height = 0,
max_height = Inf,
zscale = 1,
lit = TRUE,
heightmap = NULL,
baseshape = "rectangle",
angle = c(0, 0, 0),
clear_previous = FALSE,
...
)Arguments
- lat
Vector of latitudes (or other coordinate in the same coordinate reference system as extent).
- long
Vector of longitudes (or other coordinate in the same coordinate reference system as extent).
- extent
Either an object representing the spatial extent of the 3D scene (either from the
raster,terra,sf, orsppackages), a length-4 numeric vector specifyingc("xmin", "xmax", "ymin", "ymax"), or the spatial object (from the previously aforementioned packages) which will be automatically converted to an extent object.- type
Default
"basic". Type of tree. Other built-in option:"cone".- custom_obj_tree
Default
NULL. Instead of using the built-in types, users can also load a custom tree model in OBJ format. This function loads and manipulates the model, assuming the tree model's trunk begins at the origin. Color and specific trunk/crown proportions will be fixed to the model specified, although the overall scale can be changed per-tree viacrown_height.- custom_obj_crown
Default
NULL. Instead of using the built-in types, users can also load a custom crown model in OBJ format. This function loads a crown model and allows you to control the crown and trunk proportions separately.- custom_obj_trunk
Default
NULL. Instead of using the built-in types, users can also load a custom trunk model in OBJ format. This function loads a trunk model and allows you to control the crown and trunk proportions separately.- crown_color
Default
"darkgreen". Color(s) of the crown.- trunk_color
Default
"#964B00"(brown). Color(s) of the trunk,- absolute_height
Default
FALSE. Default is specifying the tree height directly, relative to the underlying height map. IfTRUE,crown_heightwill specified by the actual altitude of the top of the tree. Total tree height will becrown_height + trunk_height.- tree_height
Default
NULL. Height of the tree, automatically set to10if not specified. Ifabsolute_height = TRUE, then this is interpreted as the altitude of the top of the tree in the coordinate reference system used. Ifabsolute_height = FALSE, then this is interpreted as the height of the tree relative to the underlying heightmap.- trunk_height_ratio
Default
NULL. The ratio of the height of the trunk to the total height of the tree. Default is 1/3rd the crown height iftype = "basic", and 1/6th the crown height iftype = "cone".- crown_width_ratio
Default
NULL. Ratio of the crown width to the crown height. A value of1is spherical.- crown_width
Default
NULL. As an alternative to specifying the ratio, you can use this argument to specify the crown width directly.- trunk_radius
Default
NULL, automatically computed. Default is 1/5rd the trunk height iftype = "basic", and 1/10th the trunk height iftype = "cone".- tree_zscale
Default
TRUE. Whether to scale the size of the tree by zscale to have it match the size of the map. If zscale is very big, this will make the trees very small.- min_height
Default
NULL. Minimum height of a tree. Set to a positive number to filter out trees below that height.- max_height
Default
NA. Maximum height of a tree. Set to a positive number to filter out trees above that height.- zscale
Default
1. The ratio between the x and y spacing (which are assumed to be equal) and the z axis in the original heightmap.- lit
Default
TRUE. Whether to apply lighting to the tree.- heightmap
Default
NULL. Automatically extracted from the rgl window–only use if auto-extraction of matrix extent isn't working. A two-dimensional matrix, where each entry in the matrix is the elevation at that point. All points are assumed to be evenly spaced.- baseshape
Default
rectangle. Shape of the base. Options arec("rectangle","circle","hex").- angle
Default
c(0,0,0). Angle of rotation around the x, y, and z axes. If this is a matrix or list, each row (or list entry) specifies the rotation of the nth tree specified (number of rows/length of list must equal the length oflat/long).- clear_previous
Default
FALSE. IfTRUE, it will clear all existing trees.- ...
Additional arguments to pass to
rgl::triangles3d().
Examples
if(run_documentation()) {
#Let's first start by drawing some trees in a circle around Monterey Bay
#We won't scale these to a realistic size (yet)
moss_landing_coord = c(36.806807, -121.793332)
montereybay |>
sphere_shade() |>
plot_3d(montereybay,zscale=50,water=TRUE,
shadowcolor="#40310a", background = "tan",
theta=210, phi=22, zoom=0.20, fov=55)
t = seq(0,2*pi,length.out=20)
circle_coords_lat = moss_landing_coord[1] + 0.3 * sin(t)
circle_coords_long = moss_landing_coord[2] + 0.3 * cos(t)
render_tree(extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), heightmap = montereybay,
tree_zscale = FALSE, tree_height = 30, lit = TRUE,
lat = unlist(circle_coords_lat), long = unlist(circle_coords_long), zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}
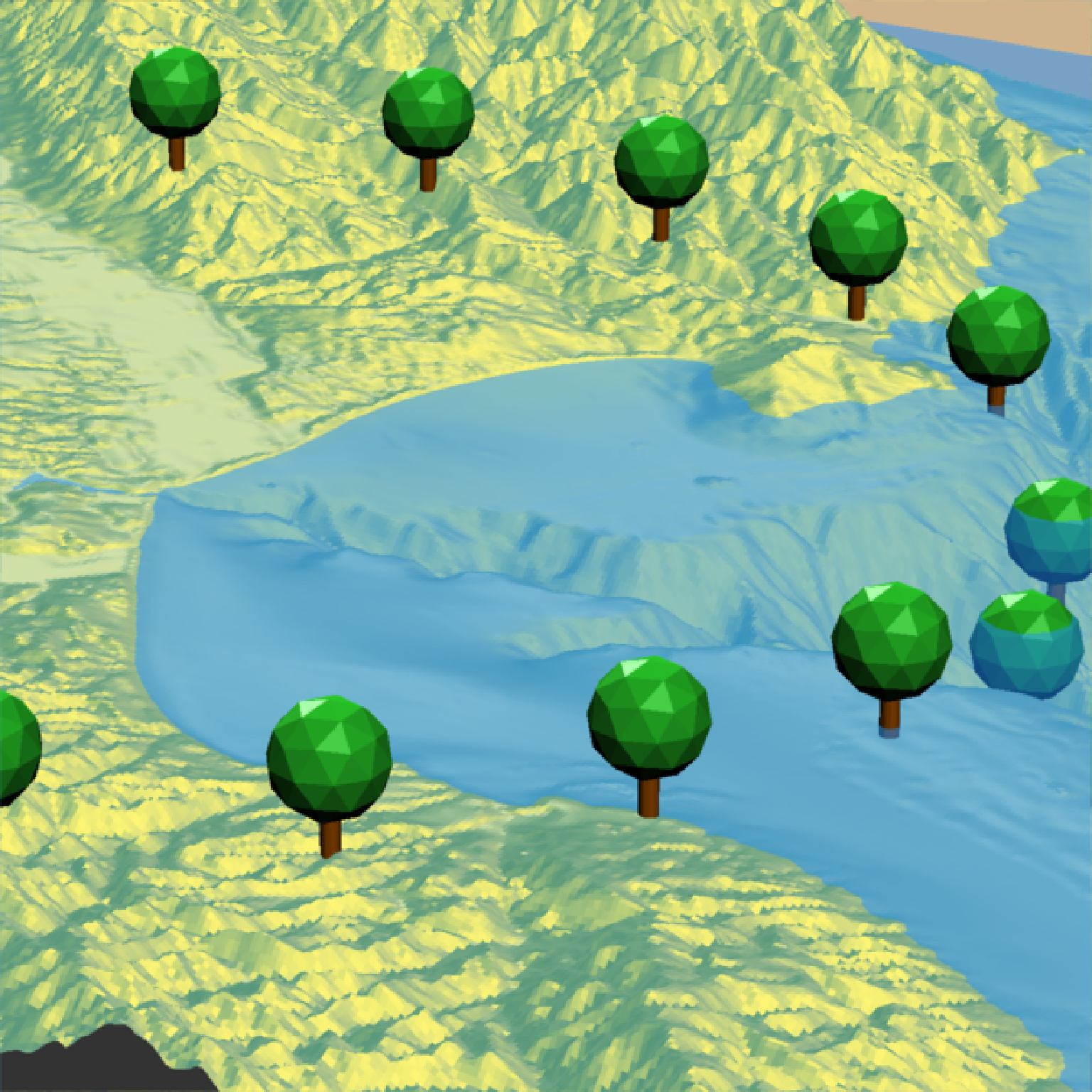 if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the crown width ratio (compared to the height)
render_tree(extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), heightmap = montereybay,
tree_zscale = FALSE, tree_height = 60, crown_width_ratio = 0.5,
clear_previous = TRUE,
lat = unlist(circle_coords_lat), long = unlist(circle_coords_long), zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the crown width ratio (compared to the height)
render_tree(extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), heightmap = montereybay,
tree_zscale = FALSE, tree_height = 60, crown_width_ratio = 0.5,
clear_previous = TRUE,
lat = unlist(circle_coords_lat), long = unlist(circle_coords_long), zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}
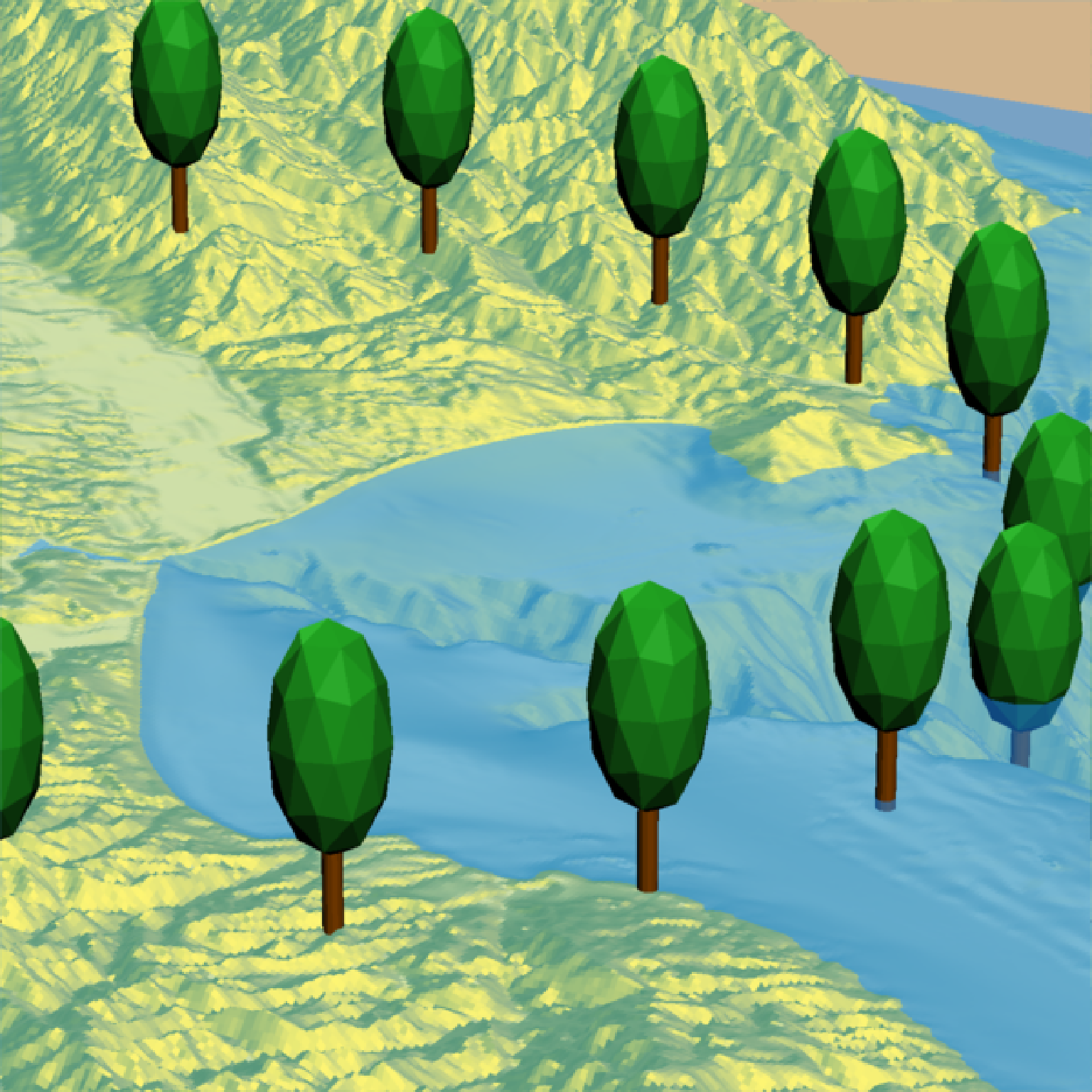 if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the trunk height and width
render_tree(extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), heightmap = montereybay,
tree_zscale = FALSE, tree_height = 40, crown_width_ratio = 2,
clear_previous = TRUE, trunk_height_ratio=1/2, trunk_radius = 1.5,
lat = unlist(circle_coords_lat), long = unlist(circle_coords_long), zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the trunk height and width
render_tree(extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), heightmap = montereybay,
tree_zscale = FALSE, tree_height = 40, crown_width_ratio = 2,
clear_previous = TRUE, trunk_height_ratio=1/2, trunk_radius = 1.5,
lat = unlist(circle_coords_lat), long = unlist(circle_coords_long), zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}
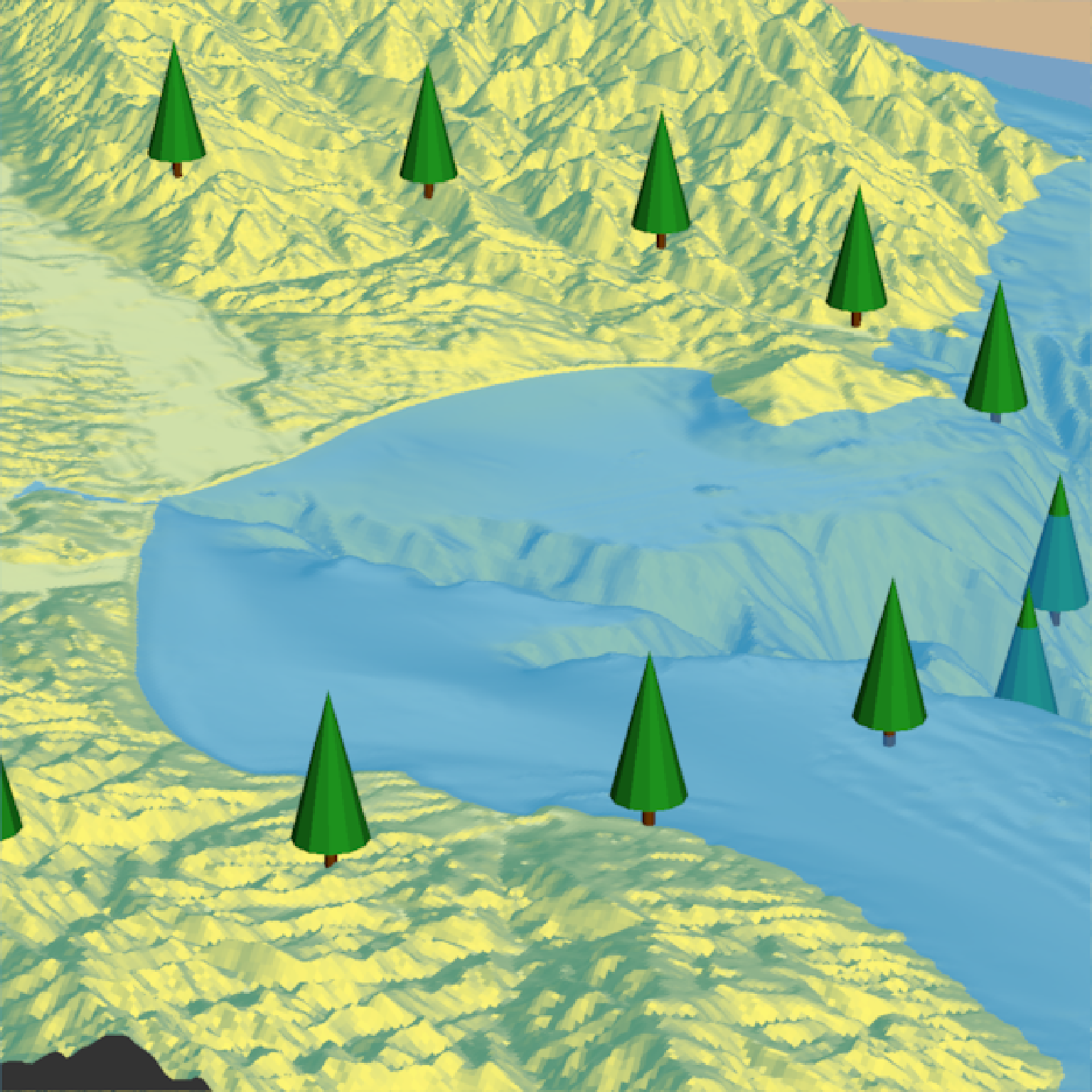
 if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the tree type
render_tree(extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), heightmap = montereybay,
tree_zscale = FALSE, tree_height = 30,
clear_previous = TRUE, type = "cone",trunk_height_ratio = 1/6,
lat = unlist(circle_coords_lat), long = unlist(circle_coords_long), zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the tree type
render_tree(extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), heightmap = montereybay,
tree_zscale = FALSE, tree_height = 30,
clear_previous = TRUE, type = "cone",trunk_height_ratio = 1/6,
lat = unlist(circle_coords_lat), long = unlist(circle_coords_long), zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}
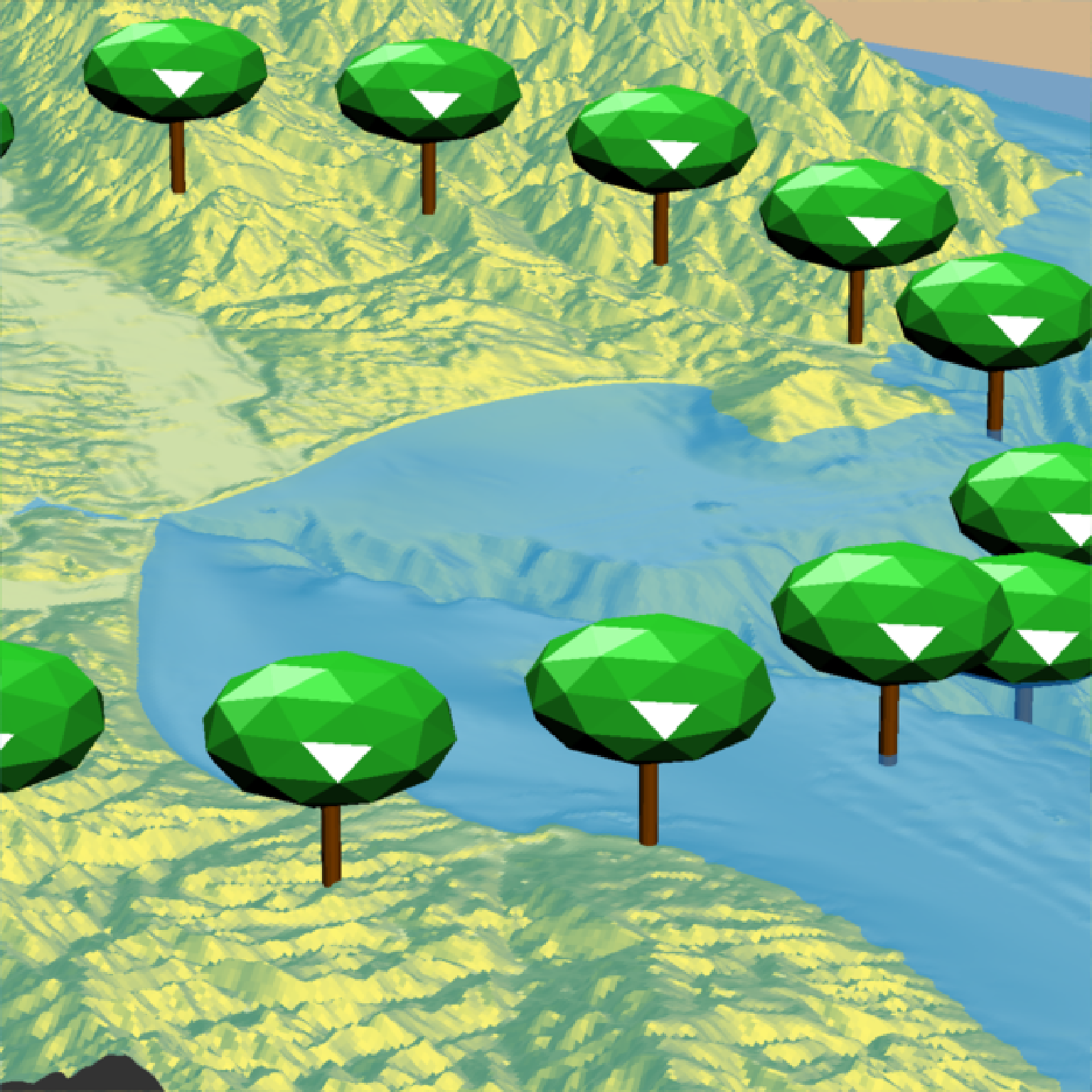
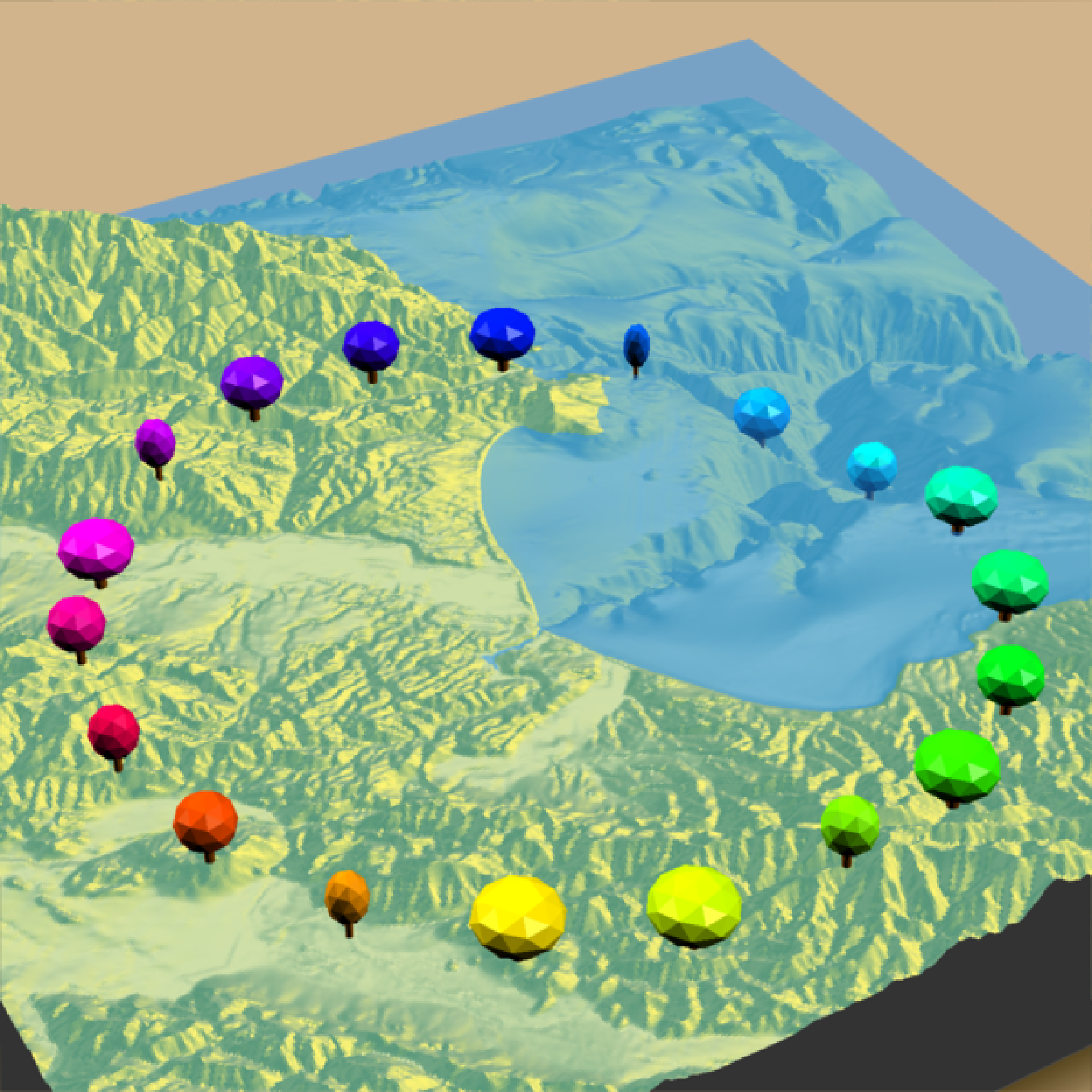
 if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the crown color:
render_camera(theta = 150, phi = 38, zoom = 0.4, fov = 55)
render_tree(extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), heightmap = montereybay,
tree_zscale = FALSE, tree_height = 30, crown_width_ratio = 0.5 + runif(20),
crown_color = rainbow(20), clear_previous = TRUE,
lat = unlist(circle_coords_lat), long = unlist(circle_coords_long), zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Change the crown color:
render_camera(theta = 150, phi = 38, zoom = 0.4, fov = 55)
render_tree(extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), heightmap = montereybay,
tree_zscale = FALSE, tree_height = 30, crown_width_ratio = 0.5 + runif(20),
crown_color = rainbow(20), clear_previous = TRUE,
lat = unlist(circle_coords_lat), long = unlist(circle_coords_long), zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}
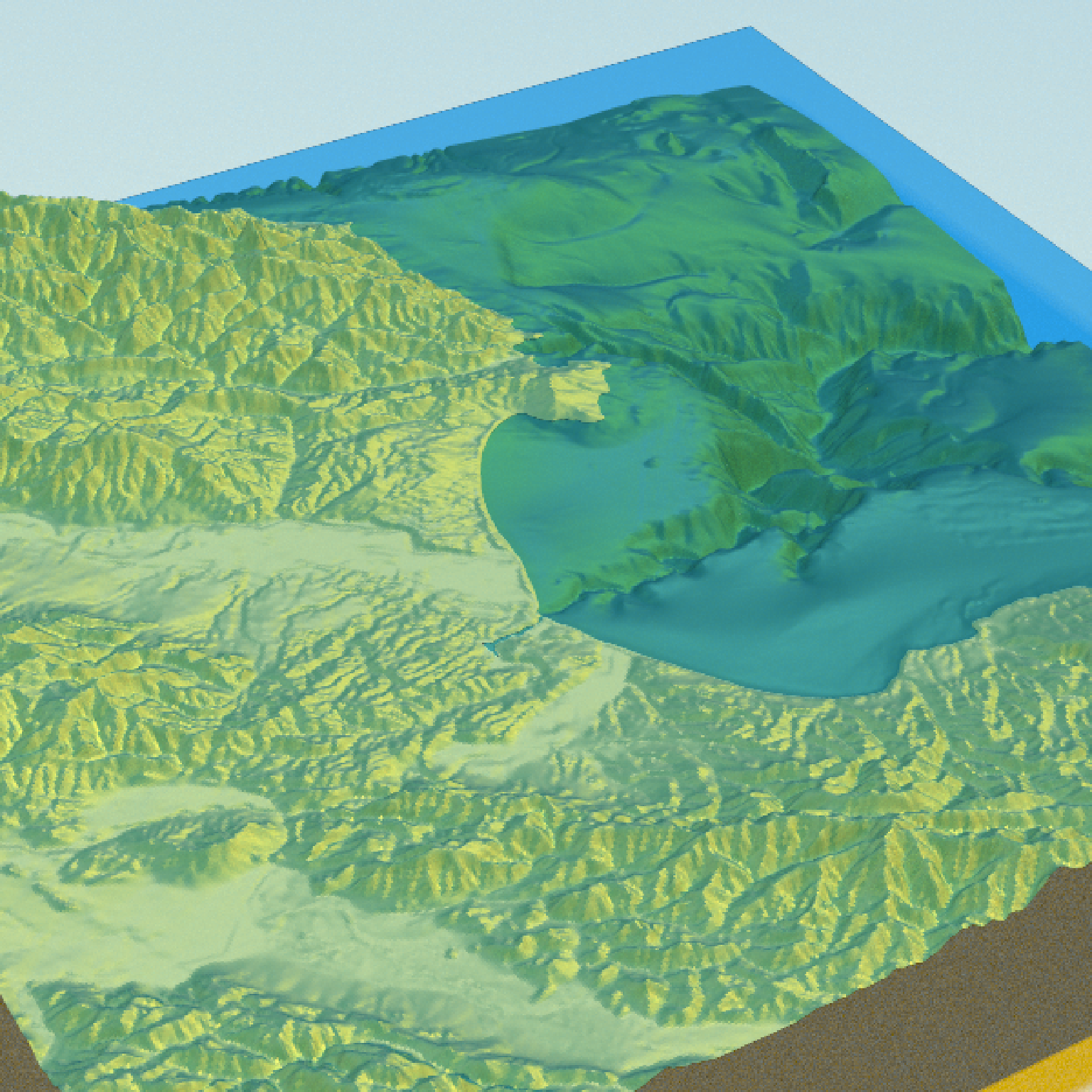
 #We will use the lidR package to generate a DEM and detect the crown tops of trees, and
#then use rayshader to render 3D tree models scaled to those heights on the map.
run_example = length(find.package("lidR", quiet = TRUE)) > 0 &&
length(find.package("sf", quiet = TRUE)) > 0 &&
length(find.package("terra", quiet = TRUE)) > 0 &&
run_documentation()
if (run_example) {
#Load the example data from the lidR package
LASfile = system.file("extdata", "Topography.laz", package="lidR")
las = lidR::readLAS(LASfile, filter = "-inside 273450 5274350 273550 5274450")
#Convert the lidar point data to a DEM and detect the location of trees from the same data
dem = lidR::rasterize_terrain(las, algorithm = lidR::tin())
tree_top_data = lidR::locate_trees(las, lidR::lmf(ws = 5))
tree_locations = sf::st_coordinates(tree_top_data)
#Convert DEM to a matrix and extract the extent of the scene
dem_matrix = raster_to_matrix(dem)
dem_extent = terra::ext(dem)
extent_values = dem_extent@pntr$vector
#Plot the ground
dem_matrix |>
height_shade() |>
add_shadow(texture_shade(dem_matrix),0.2) |>
add_shadow(lamb_shade(dem_matrix),0) |>
plot_3d(dem_matrix, windowsize = 800)
render_snapshot()
}
#>
#We will use the lidR package to generate a DEM and detect the crown tops of trees, and
#then use rayshader to render 3D tree models scaled to those heights on the map.
run_example = length(find.package("lidR", quiet = TRUE)) > 0 &&
length(find.package("sf", quiet = TRUE)) > 0 &&
length(find.package("terra", quiet = TRUE)) > 0 &&
run_documentation()
if (run_example) {
#Load the example data from the lidR package
LASfile = system.file("extdata", "Topography.laz", package="lidR")
las = lidR::readLAS(LASfile, filter = "-inside 273450 5274350 273550 5274450")
#Convert the lidar point data to a DEM and detect the location of trees from the same data
dem = lidR::rasterize_terrain(las, algorithm = lidR::tin())
tree_top_data = lidR::locate_trees(las, lidR::lmf(ws = 5))
tree_locations = sf::st_coordinates(tree_top_data)
#Convert DEM to a matrix and extract the extent of the scene
dem_matrix = raster_to_matrix(dem)
dem_extent = terra::ext(dem)
extent_values = dem_extent@pntr$vector
#Plot the ground
dem_matrix |>
height_shade() |>
add_shadow(texture_shade(dem_matrix),0.2) |>
add_shadow(lamb_shade(dem_matrix),0) |>
plot_3d(dem_matrix, windowsize = 800)
render_snapshot()
}
#>
 if (run_example) {
#The tree locations are given as an absolute height (as opposed to relative to the surface)
#so we set `absolute_height = TRUE`.
render_tree(lat = tree_locations[,2],
long = tree_locations[,1],
crown_width_ratio = 0.5,
absolute_height = TRUE,
tree_height = tree_locations[,3],
trunk_height_ratio = 0.2 + 0.1*runif(nrow(tree_locations)),
crown_color = "#00aa00",
extent = raster::extent(extent_values),
heightmap = dem_matrix,
clear_previous = TRUE)
#Remove existing lights and add our own with rgl
rgl::pop3d("lights")
rgl::light3d(phi=35,theta=90, viewpoint.rel=F, diffuse="#ffffff", specular="#000000")
rgl::light3d(phi=-45,theta=-40, viewpoint.rel=F, diffuse="#aaaaaa", specular="#000000")
render_snapshot()
}
if (run_example) {
#The tree locations are given as an absolute height (as opposed to relative to the surface)
#so we set `absolute_height = TRUE`.
render_tree(lat = tree_locations[,2],
long = tree_locations[,1],
crown_width_ratio = 0.5,
absolute_height = TRUE,
tree_height = tree_locations[,3],
trunk_height_ratio = 0.2 + 0.1*runif(nrow(tree_locations)),
crown_color = "#00aa00",
extent = raster::extent(extent_values),
heightmap = dem_matrix,
clear_previous = TRUE)
#Remove existing lights and add our own with rgl
rgl::pop3d("lights")
rgl::light3d(phi=35,theta=90, viewpoint.rel=F, diffuse="#ffffff", specular="#000000")
rgl::light3d(phi=-45,theta=-40, viewpoint.rel=F, diffuse="#aaaaaa", specular="#000000")
render_snapshot()
}
 if (run_example) {
#Render tree also works with `render_highquality()`
render_highquality(lightdirection=c(90,45),lightaltitude=c(90,45),
lightcolor=c("dodgerblue","orange"), samples = 32,
min_variance = 0)
}
if (run_example) {
#Render tree also works with `render_highquality()`
render_highquality(lightdirection=c(90,45),lightaltitude=c(90,45),
lightcolor=c("dodgerblue","orange"), samples = 32,
min_variance = 0)
}
