Adds MULTIPOLYGONZ will be plotted in the coordinate system set by the user-specified
extent argument as-is.
You can also use save_multipolygonz_to_obj() manually to convert sf objects
render_multipolygonz(
sfobj,
extent = NULL,
zscale = 1,
heightmap = NULL,
color = "grey50",
offset = 0,
obj_zscale = TRUE,
swap_yz = TRUE,
clear_previous = FALSE,
baseshape = "rectangle",
rgl_tag = "_multipolygon",
...
)Arguments
- sfobj
An sf object with MULTIPOLYGON Z geometry.
- extent
Either an object representing the spatial extent of the scene (either from the
raster,terra,sf, orsppackages), a length-4 numeric vector specifyingc("xmin", "xmax","ymin","ymax"), or the spatial object (from the previously aforementioned packages) which will be automatically converted to an extent object.- zscale
Default
1. The ratio between the x and y spacing (which are assumed to be equal) and the z axis in the original heightmap.- heightmap
Default
NULL. Automatically extracted from the rgl window–only use if auto-extraction of matrix extent isn't working. A two-dimensional matrix, where each entry in the matrix is the elevation at that point. All points are assumed to be evenly spaced.- color
Default
black. Color of the 3D model, ifload_material = FALSE.- offset
Default
5. Offset of the track from the surface, ifaltitude = NULL.- obj_zscale
Default
TRUE. Whether to scale the size of the OBJ by zscale to have it match the size of the map. If zscale is very big, this will make the model very small.- swap_yz
Default
TRUE. Whether to swap and Y and Z axes. (Y axis is vertical in rayshader coordinates, but data is often provided with Z being vertical).- clear_previous
Default
FALSE. IfTRUE, it will clear all existing points.- baseshape
Default
rectangle. Shape of the base. Options arec("rectangle","circle","hex").- rgl_tag
Default
"". Tag to add to the rgl scene id, will be prefixed by"obj"- ...
Additional arguments to pass to
rgl::triangles3d().
Examples
run_examples = length(find.package("sf", quiet = TRUE)) &&
length(find.package("elevatr", quiet = TRUE)) &&
length(find.package("raster", quiet = TRUE)) &&
run_documentation()
if(run_examples) {
library(sf)
#Set location of washington monument
washington_monument_location = st_point(c(-77.035249, 38.889462))
wm_point = washington_monument_location |>
st_point() |>
st_sfc(crs = 4326) |>
st_transform(st_crs(washington_monument_multipolygonz))
elevation_data = elevatr::get_elev_raster(locations = wm_point, z = 14)
scene_bbox = st_bbox(st_buffer(wm_point,300))
cropped_data = raster::crop(elevation_data, scene_bbox)
#Use rayshader to convert that raster data to a matrix
dc_elevation_matrix = raster_to_matrix(cropped_data)
#Remove negative elevation data
dc_elevation_matrix[dc_elevation_matrix < 0] = 0
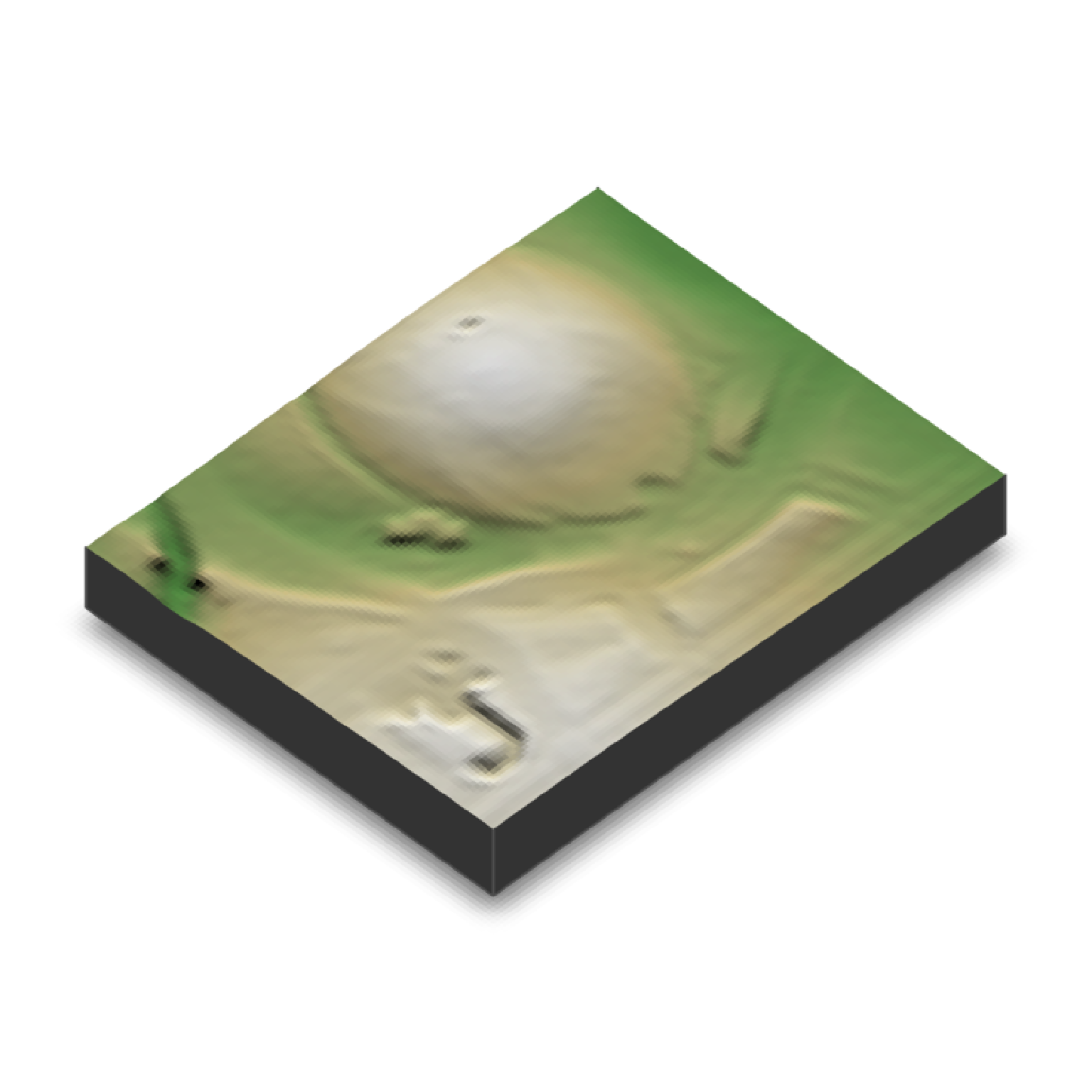
#Plot a 3D map of the national mall
dc_elevation_matrix |>
height_shade() |>
add_shadow(lamb_shade(dc_elevation_matrix), 0) |>
plot_3d(dc_elevation_matrix, zscale=3.7, water = TRUE, waterdepth = 1,
soliddepth=-50, windowsize = 800)
render_snapshot()
}
#> Mosaicing & Projecting
#> Note: Elevation units are in meters.
#> Warning: No water rendered--all elevations above or equal to water level. Range of heights: 2.55567121505737-12.3973035812378. Depth specified: 1
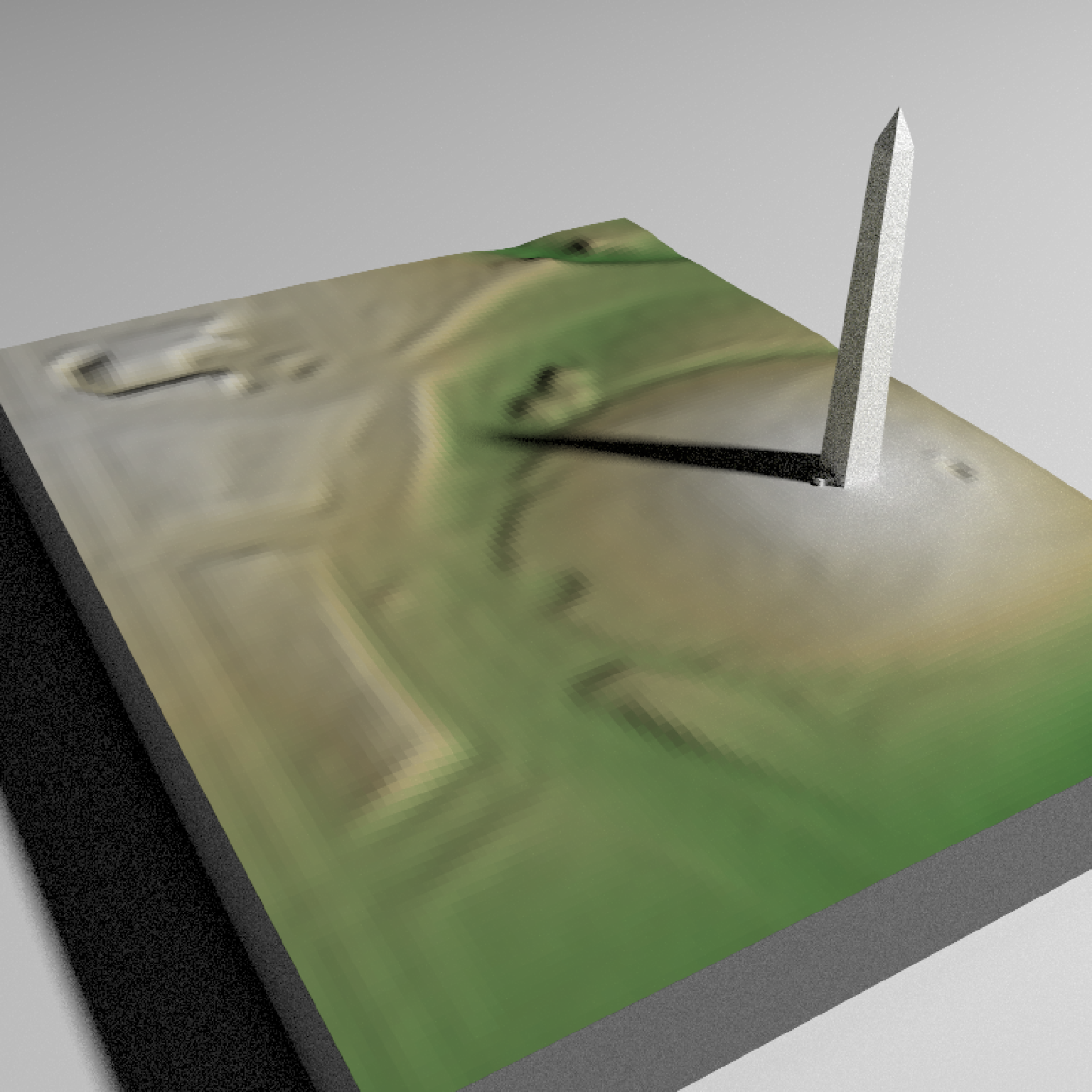
 if(run_examples) {
#Zoom in on the monument
render_camera(theta=150, phi=35, zoom= 0.55, fov=70)
#Render the national monument
rgl::par3d(ignoreExtent = TRUE)
render_multipolygonz(washington_monument_multipolygonz,
extent = raster::extent(cropped_data),
zscale = 4, color = "grey80",
heightmap = dc_elevation_matrix)
render_snapshot()
}
if(run_examples) {
#Zoom in on the monument
render_camera(theta=150, phi=35, zoom= 0.55, fov=70)
#Render the national monument
rgl::par3d(ignoreExtent = TRUE)
render_multipolygonz(washington_monument_multipolygonz,
extent = raster::extent(cropped_data),
zscale = 4, color = "grey80",
heightmap = dc_elevation_matrix)
render_snapshot()
}
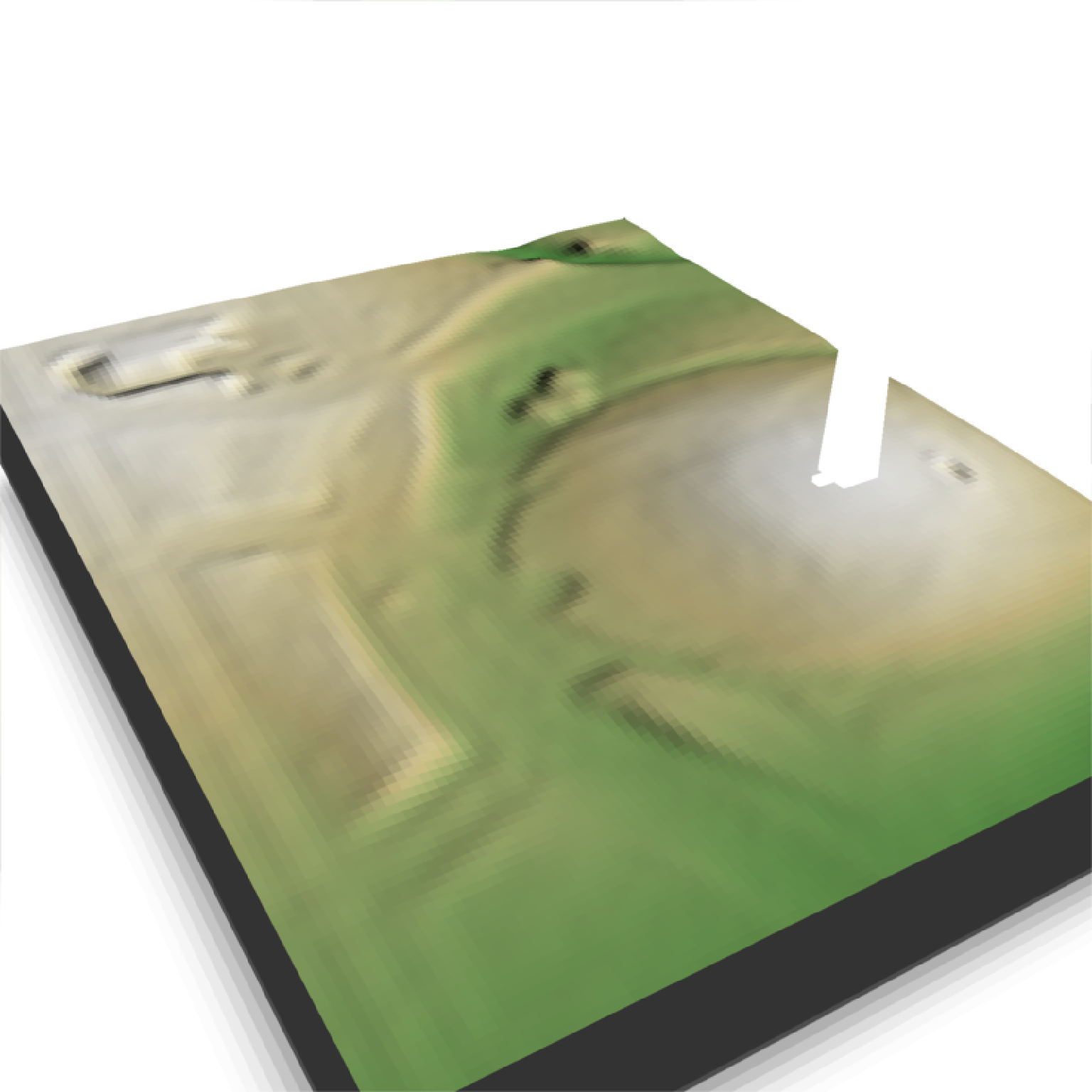 if(run_examples) {
#This works with `render_highquality()`
render_highquality(min_variance = 0, samples = 16)
}
if(run_examples) {
#This works with `render_highquality()`
render_highquality(min_variance = 0, samples = 16)
}