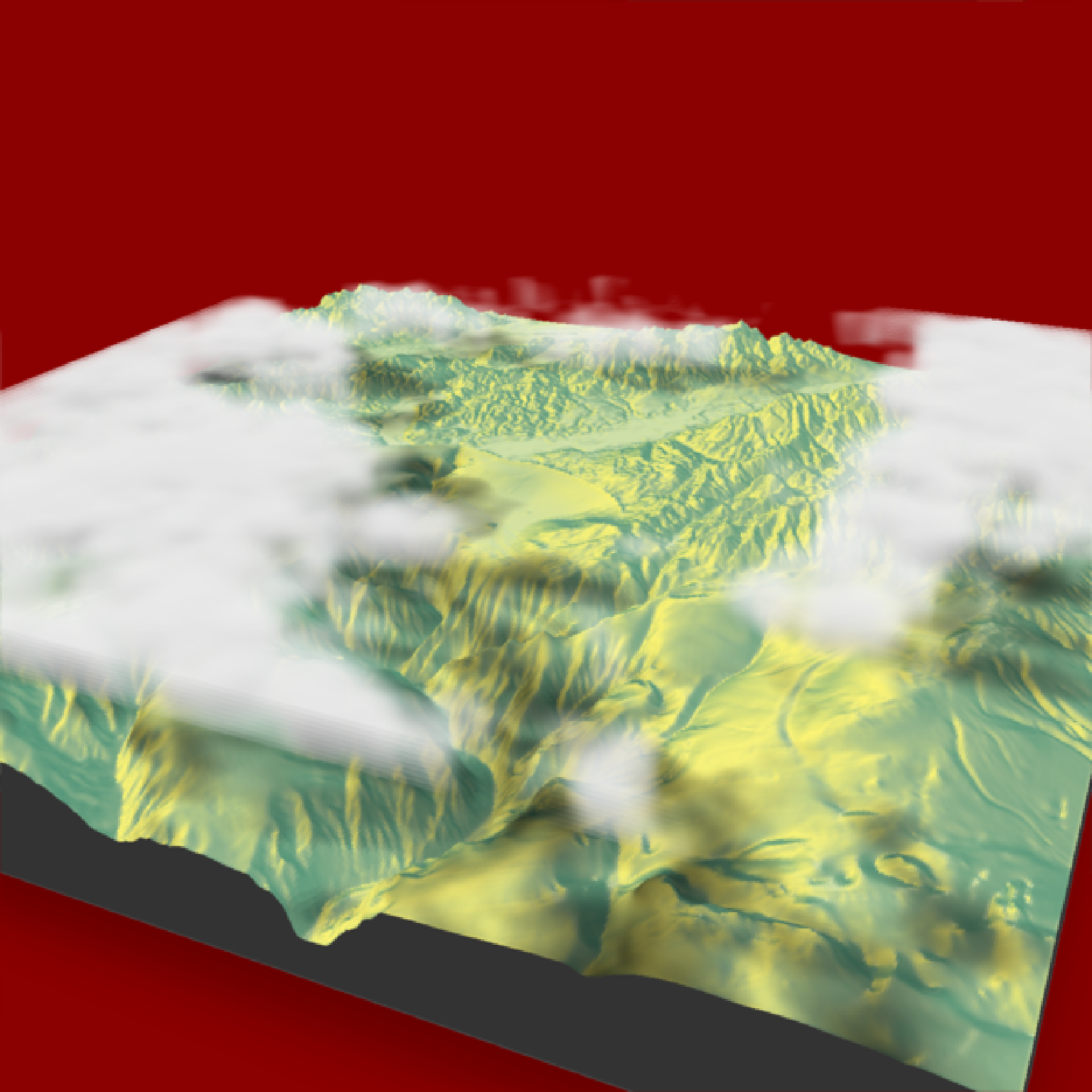
Render shadows from the 3D floating cloud layer on the ground. Use this function
to add shadows to the map with the add_shadow() function.
For realistic results, argument should match those passed to render_clouds(). The exception to this
is attenuation_coef, which can be used to adjust the darkness of the resulting shadows.
cloud_shade(
heightmap,
start_altitude = 1000,
end_altitude = 2000,
sun_altitude = 90,
sun_angle = 315,
time = 0,
cloud_cover = 0.5,
layers = 10,
offset_x = 0,
offset_y = 0,
scale_x = 1,
scale_y = 1,
scale_z = 1,
frequency = 0.005,
fractal_levels = 16,
attenuation_coef = 1,
seed = 1,
zscale = 1
)Arguments
- heightmap
A two-dimensional matrix, where each entry in the matrix is the elevation at that point. This is used by
render_clouds()to calculate the regions the clouds should be rendered in.- start_altitude
Default
1000. The bottom of the cloud layer.- end_altitude
Default
2000. The top of the cloud layer.- sun_altitude
Default
10. The angle, in degrees (as measured from the horizon) from which the light originates.- sun_angle
Default
315(NW). The angle, in degrees, around the matrix from which the light originates. Zero degrees is North, increasing clockwise- time
Default
0. Advance this to make the clouds evolve and change in shape.- cloud_cover
Default
0.5. The percentage of cloud cover.- layers
Default
90. The number of layers to render the cloud layer.- offset_x
Default
0. Change this to move the cloud layer sideways.- offset_y
Default
0. Change this to move the cloud layer backwards and forward- scale_x
Default
1. Scale the fractal pattern in the x direction.- scale_y
Default
1. Scale the fractal pattern in the y direction.- scale_z
Default
1. Scale the fractal pattern in the z (altitude) direction. (automatically calculated). Scale the fractal pattern in the z (vertical) direction. s.- frequency
Default
0.005. The base frequency of the noise used to calculate the fractal cloud structure.- fractal_levels
Default
16. The fractal dimension used to calculate the noise. Higher values give more fine structure, but take longer to calculate.- attenuation_coef
Default
1. Amount of attenuation in the cloud (higher numbers give darker shadows). This value is automatically scaled to account for increasing the number of layers.- seed
Default
1. Random seed used to generate clouds.- zscale
Default
1. The ratio between the x and y spacing (which are assumed to be equal) and the z axis. For example, if the elevation levels are in units of 1 meter and the grid values are separated by 10 meters,zscalewould be 10.
Value
A 2D shadow matrix.
Examples
if(run_documentation()) {
#Render clouds with cloud shadows on the ground
montereybay |>
sphere_shade() |>
add_shadow(cloud_shade(montereybay,zscale=50), 0.0) |>
plot_3d(montereybay,background="darkred",zscale=50)
render_camera(theta=-65, phi = 25, zoom = 0.45, fov = 80)
render_clouds(montereybay, zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}
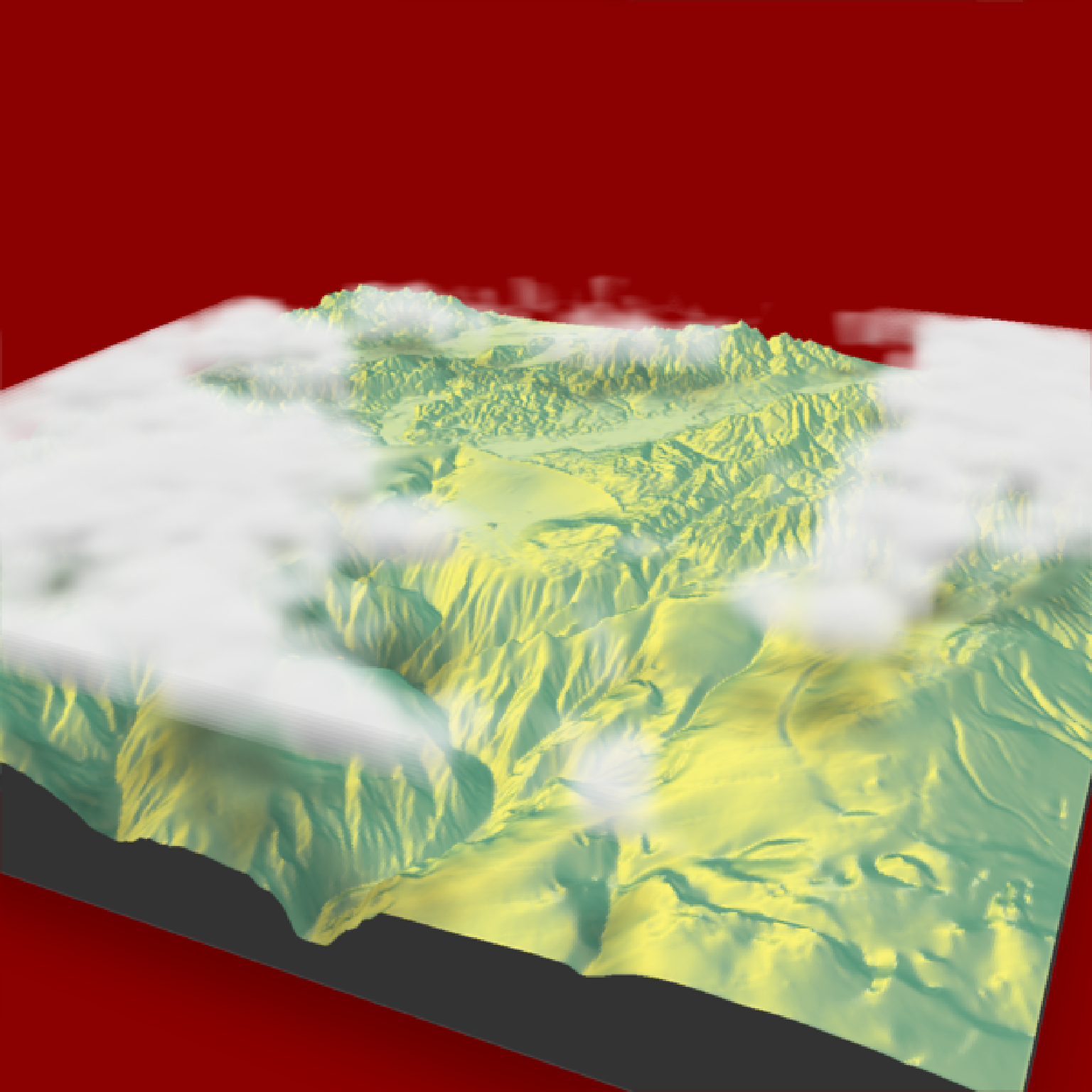 if(run_documentation()) {
#Adjust the light direction for shadows and increase the attenuation for darker clouds
montereybay |>
sphere_shade() |>
add_shadow(cloud_shade(montereybay,zscale=50, sun_altitude=20, attenuation_coef = 3), 0.0) |>
plot_3d(montereybay,background="darkred",zscale=50)
render_camera(theta=-65, phi = 25, zoom = 0.45, fov = 80)
render_clouds(montereybay, zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}
if(run_documentation()) {
#Adjust the light direction for shadows and increase the attenuation for darker clouds
montereybay |>
sphere_shade() |>
add_shadow(cloud_shade(montereybay,zscale=50, sun_altitude=20, attenuation_coef = 3), 0.0) |>
plot_3d(montereybay,background="darkred",zscale=50)
render_camera(theta=-65, phi = 25, zoom = 0.45, fov = 80)
render_clouds(montereybay, zscale=50)
render_snapshot()
}