Adds beveled polygon to the scene using the raybevel package. See
the raybevel::generate_beveled_polygon() function for more information.
render_beveled_polygons(
polygon,
extent,
material = "grey",
bevel_material = NA,
angle = 45,
bevel_width = 5,
width_raw_units = FALSE,
bevel = NA,
zscale = 1,
bevel_height = 1,
base_height = 0,
raw_heights = FALSE,
raw_offsets = FALSE,
heights_relative_to_centroid = TRUE,
set_max_height = FALSE,
max_height = 10,
scale_all_max = TRUE,
data_column_top = NULL,
data_column_bottom = NULL,
heightmap = NULL,
scale_data = 1,
holes = 0,
alpha = 1,
lit = TRUE,
flat_shading = FALSE,
light_altitude = c(45, 30),
light_direction = c(315, 225),
light_intensity = 1,
light_relative = FALSE,
clear_previous = FALSE,
...
)Arguments
- polygon
sfobject, "SpatialPolygon"spobject, or xy coordinates of polygon represented in a way that can be processed byxy.coords(). If xy-coordinate based polygons are open, they will be closed by adding an edge from the last point to the first.- extent
Either an object representing the spatial extent of the 3D scene (either from the
raster,terra,sf, orsppackages), a length-4 numeric vector specifyingc("xmin", "xmax", "ymin", "ymax"), or the spatial object (from the previously aforementioned packages) which will be automatically converted to an extent object.- material
Default
"grey80". If a color string, this will specify the color of the sides/base of the polygon. Alternatively (for more customization), this can be a rayvertex::material_list()object to specify the full color/appearance/material options for the resultingray_meshmesh.- bevel_material
Default
NA, defaults to the material specified inmaterial. If a color string, this will specify the color of the polygon bevel. Alternatively (for more customization), this can be arayvertex::material_list()object to specify the full color/appearance/material options for the resultingray_meshmesh.- angle
Default
45. Angle of the bevel.- bevel_width
Default
5. Width of the bevel.- width_raw_units
Default
FALSE. Whether the bevel width should be measured in raw display units, or the actual units of the map.- bevel
Default
NULL. A list withx/ycomponents that specify a bevel profile. Seeraybevel::generate_bevel()- zscale
Default
1. The ratio between the x and y spacing (which are assumed to be equal) and the z axis in the original heightmap.- bevel_height
Default
1. Height from the base of the polygon to the start of the beveled top.- base_height
Default
0. Height of the base of the polygon.- raw_heights
Default
FALSE. A logical flag indicating whether thebevel_heightsare already in raw format and do not need to be multiplied by the maximum time of the skeleton. See the documentation forraybevel::generate_beveled_polygon()for more info.- raw_offsets
Default
FALSE. A logical flag indicating whether thebevel_offsetsare already in raw format and do not need to be multiplied by the maximum time of the skeleton. See the documentation forraybevel::generate_beveled_polygon()for more info.- heights_relative_to_centroid
Default
FALSE. Whether the heights should be measured in absolute terms, or relative to the centroid of the polygon.- set_max_height
Default
FALSE. A logical flag that controls whether to set the max height of the roof based on themax_heightargument.- max_height
Default
1. The maximum height of the polygon.- scale_all_max
Default
FALSE. If passing in a list of multiple skeletons with polygons, whether to scale each polygon to the overall max height, or whether to scale each max height to the maximum internal distance in the polygon.- data_column_top
Default
NULL. A string indicating the column in thesfobject to use to specify the top of the beveled polygon.- data_column_bottom
Default
NULL. A string indicating the column in thesfobject to use to specify the bottom of the beveled polygon.- heightmap
Default
NULL. Automatically extracted from the rgl window–only use if auto-extraction of matrix extent isn't working. A two-dimensional matrix, where each entry in the matrix is the elevation at that point. All points are assumed to be evenly spaced.- scale_data
Default
1. If specifyingdata_column_topordata_column_bottom, how much to scale that value when rendering.- holes
Default
0. If passing in a polygon directly, this specifies which index represents the holes in the polygon. See theearcutfunction in thedecidopackage for more information.- alpha
Default
1. Transparency of the polygons.- lit
Default
TRUE. Whether to light the polygons.- flat_shading
Default
FALSE. Set toTRUEto have nicer shading on the 3D polygons. This comes with the slight penalty of increasing the memory use of the scene due to vertex duplication. This will not affect software or high quality renders.- light_altitude
Default
c(45, 30). Degree(s) from the horizon from which to light the polygons.- light_direction
Default
c(315, 225). Degree(s) from north from which to light the polygons.- light_intensity
Default
1. Intensity of the specular highlight on the polygons.- light_relative
Default
FALSE. Whether the light direction should be taken relative to the camera, or absolute.- clear_previous
Default
FALSE. IfTRUE, it will clear all existing polygons.- ...
Additional arguments to pass to
rgl::triangles3d().
Examples
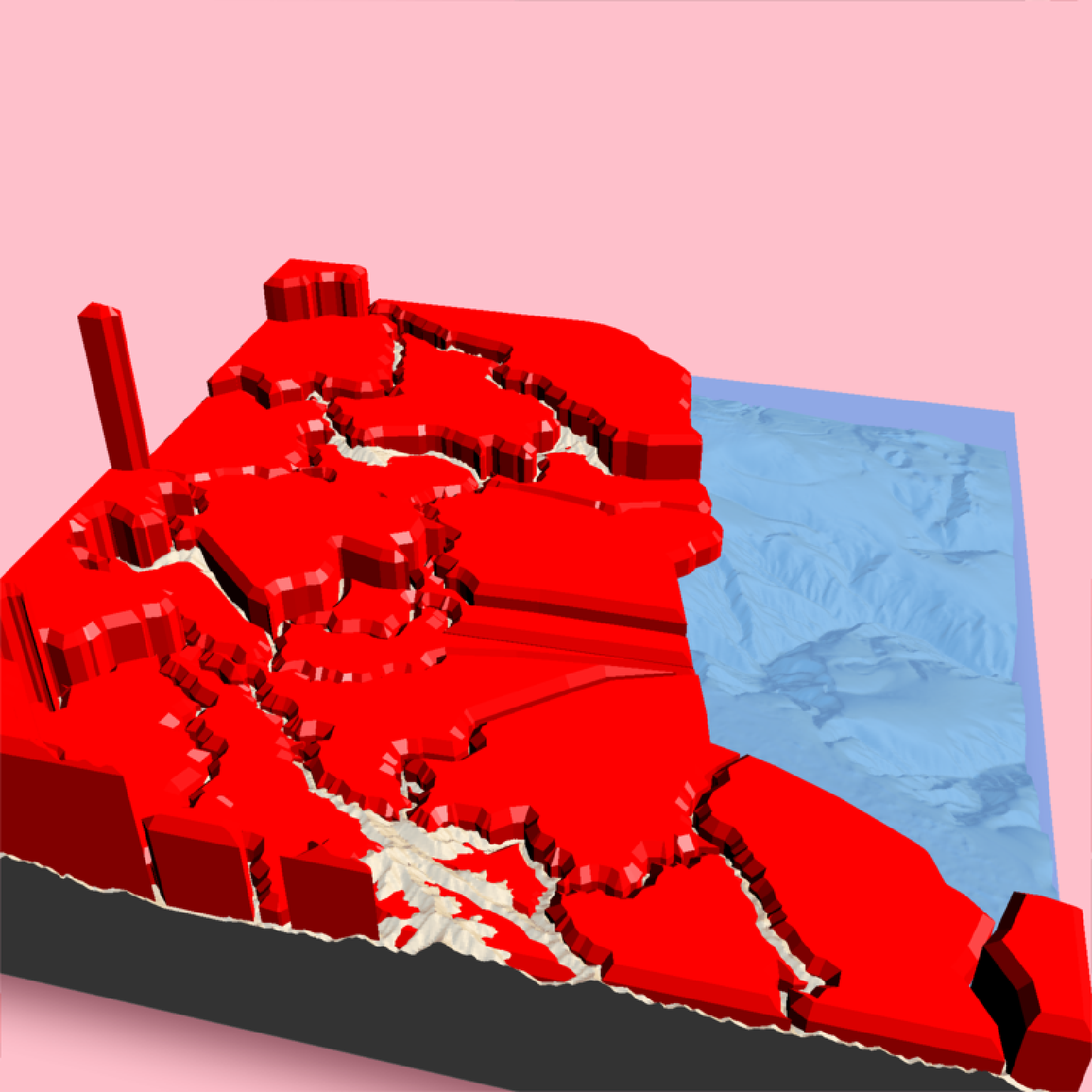
# This function can also create fake "terrain" from polygons by visualizing the distance
# to the nearest edge.
if(run_documentation()) {
#Render the county borders as polygons in Monterey Bay as terrain
montereybay |>
sphere_shade(texture = "desert") |>
add_shadow(ray_shade(montereybay,zscale = 50)) |>
plot_3d(montereybay, water = TRUE, windowsize = 800, watercolor = "dodgerblue",
background = "pink")
#We will apply a negative buffer to create space between adjacent polygons. You may
#have to call `sf::sf_use_s2(FALSE)` before running this code to get it to run.
sf::sf_use_s2(FALSE)
mont_county_buff = sf::st_simplify(sf::st_buffer(monterey_counties_sf,-0.003), dTolerance=0.001)
render_beveled_polygons(mont_county_buff, flat_shading = TRUE, angle = 45 ,
heightmap = montereybay, bevel_width=2000,
material = "red",
extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"),
bevel_height = 5000, base_height=0,
zscale=200)
render_camera(theta = 0, phi = 90, zoom = 0.65, fov = 0)
render_snapshot()
render_camera(theta=194, phi= 35, zoom = 0.5, fov= 80)
render_snapshot()
}
#> `montereybay` dataset used with no zscale--setting `zscale=50`. For a realistic depiction, raise `zscale` to 200.
#> Warning: st_buffer does not correctly buffer longitude/latitude data
#> dist is assumed to be in decimal degrees (arc_degrees).
#> Warning: st_simplify does not correctly simplify longitude/latitude data, dTolerance needs to be in decimal degrees
#> Warning: st_centroid assumes attributes are constant over geometries
#> Warning: st_centroid does not give correct centroids for longitude/latitude data
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 6.905772, calculating full polygon model
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 5.186830, calculating full polygon model
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 4.704823, calculating full polygon model
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 0.720301, calculating full polygon model

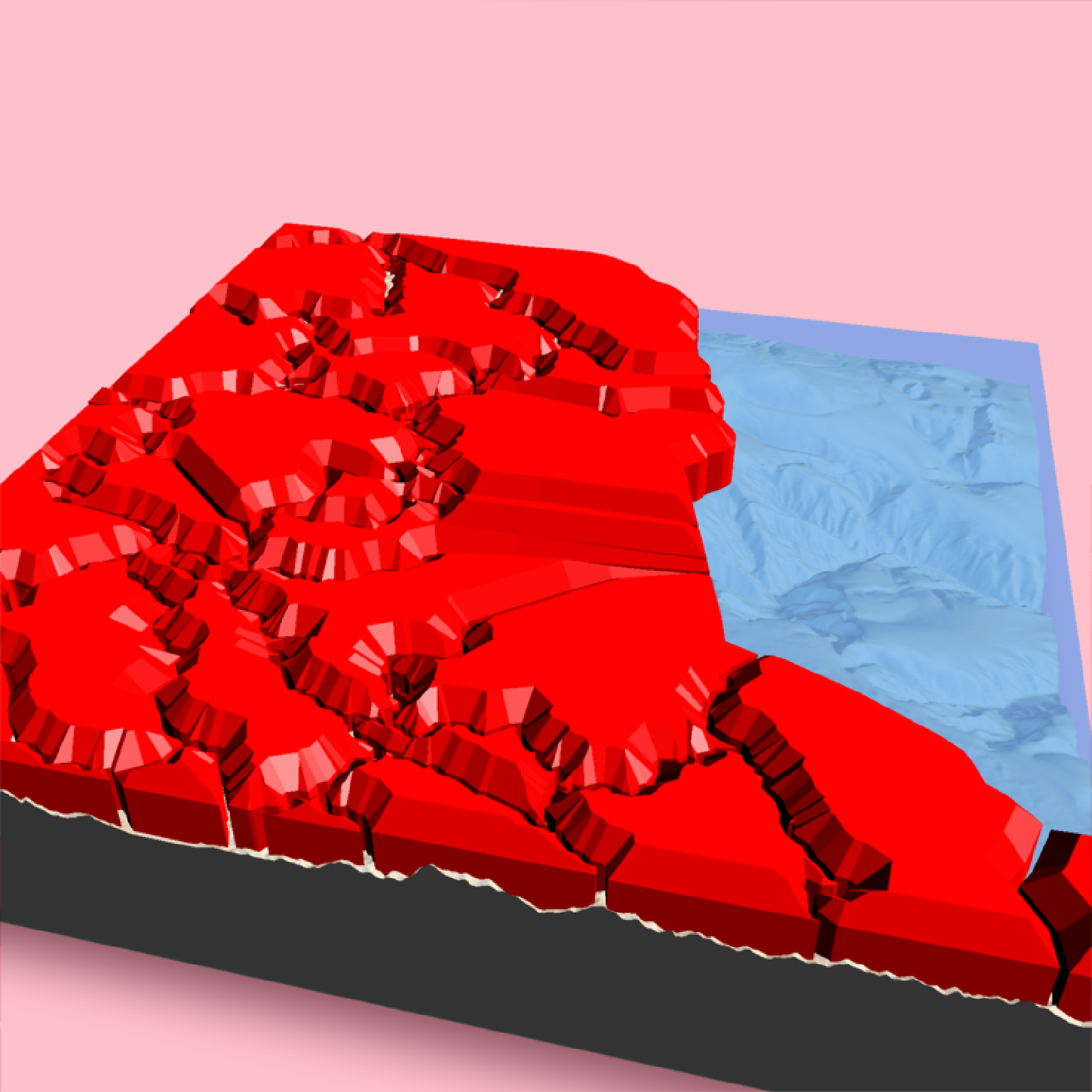 # Changing the color of the beveled top:
if(run_documentation()) {
render_beveled_polygons(mont_county_buff, flat_shading = TRUE, angle = 45 ,
heightmap = montereybay, bevel_width=2000,
material = "tan", bevel_material = "darkgreen",
extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), clear_previous=TRUE,
bevel_height = 5000, base_height=0,
zscale=200)
}
#> Warning: st_centroid assumes attributes are constant over geometries
#> Warning: st_centroid does not give correct centroids for longitude/latitude data
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 6.905772, calculating full polygon model
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 5.186830, calculating full polygon model
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 4.704823, calculating full polygon model
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 0.720301, calculating full polygon model
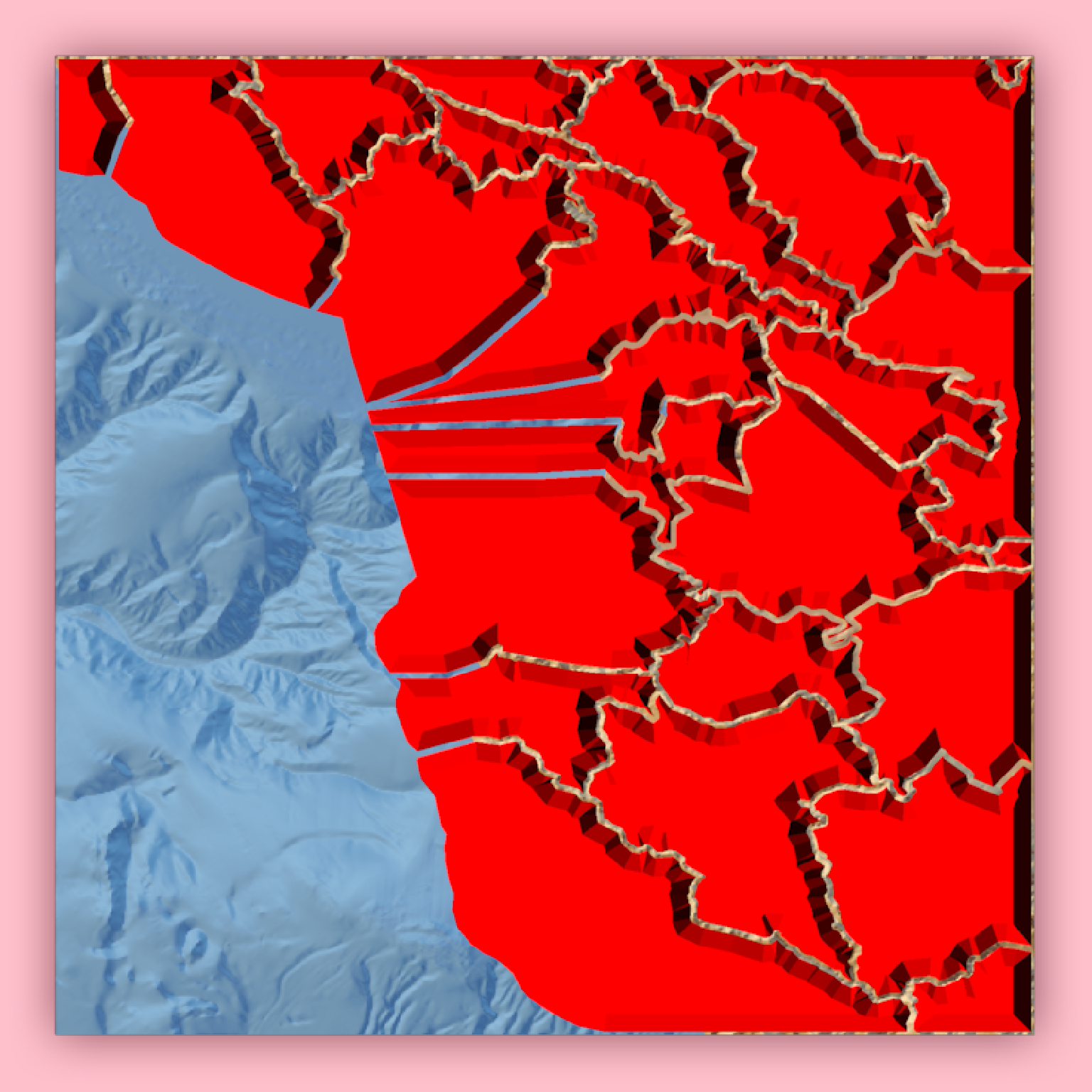
# We can create a nice curved surface by passing in a bevel generated with the
# `raybevel::generate_bevel()` function.
if(run_documentation()) {
render_beveled_polygons(mont_county_buff, flat_shading = TRUE, heightmap = montereybay,
bevel = raybevel::generate_bevel("exp",bevel_end = 0.4),
#max_height = 10, scale_all_max = TRUE, set_max_height = TRUE,
material = rayvertex::material_list(diffuse="red",
ambient = "darkred",
diffuse_intensity = 0.2,
ambient_intensity = 0.1),
light_intensity = 1, light_relative = FALSE,
extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), bevel_height = 5000,
base_height=0, clear_previous = TRUE,
zscale=200)
render_snapshot()
}
#> Warning: st_centroid assumes attributes are constant over geometries
#> Warning: st_centroid does not give correct centroids for longitude/latitude data
# Changing the color of the beveled top:
if(run_documentation()) {
render_beveled_polygons(mont_county_buff, flat_shading = TRUE, angle = 45 ,
heightmap = montereybay, bevel_width=2000,
material = "tan", bevel_material = "darkgreen",
extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), clear_previous=TRUE,
bevel_height = 5000, base_height=0,
zscale=200)
}
#> Warning: st_centroid assumes attributes are constant over geometries
#> Warning: st_centroid does not give correct centroids for longitude/latitude data
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 6.905772, calculating full polygon model
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 5.186830, calculating full polygon model
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 4.704823, calculating full polygon model
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 0.720301, calculating full polygon model
# We can create a nice curved surface by passing in a bevel generated with the
# `raybevel::generate_bevel()` function.
if(run_documentation()) {
render_beveled_polygons(mont_county_buff, flat_shading = TRUE, heightmap = montereybay,
bevel = raybevel::generate_bevel("exp",bevel_end = 0.4),
#max_height = 10, scale_all_max = TRUE, set_max_height = TRUE,
material = rayvertex::material_list(diffuse="red",
ambient = "darkred",
diffuse_intensity = 0.2,
ambient_intensity = 0.1),
light_intensity = 1, light_relative = FALSE,
extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), bevel_height = 5000,
base_height=0, clear_previous = TRUE,
zscale=200)
render_snapshot()
}
#> Warning: st_centroid assumes attributes are constant over geometries
#> Warning: st_centroid does not give correct centroids for longitude/latitude data
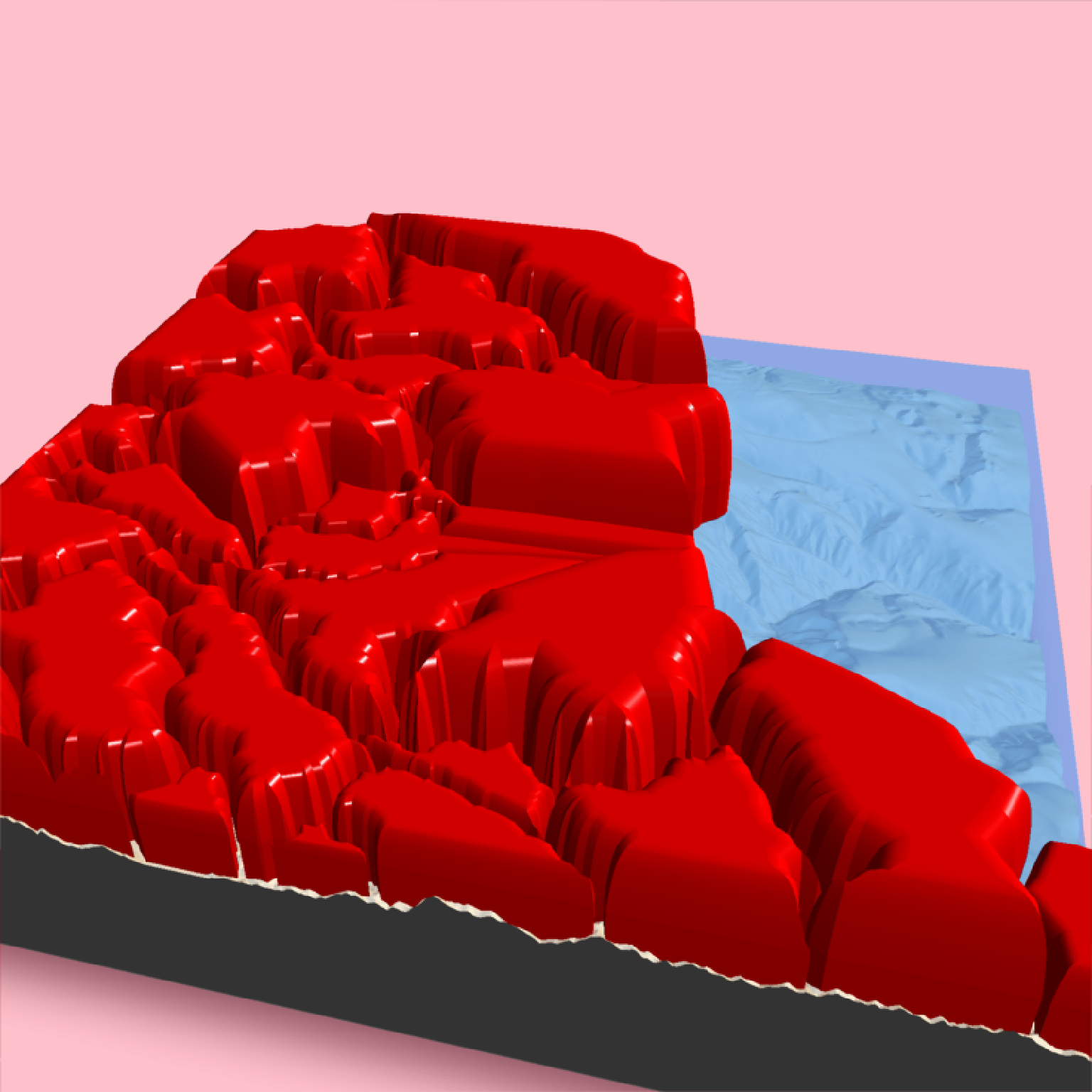 # While the bevels all start at the same point in the above example,
# they rise to different levels due to being scaled by the maximum internal distance
# in the polygon. Setting `scale_all_max = TRUE` ensures the bevels are all scaled to the
# same maximum height (in this case, 3000m above the 5000m bevel start height).
if(run_documentation()) {
render_beveled_polygons(mont_county_buff, flat_shading = TRUE, heightmap = montereybay,
bevel = raybevel::generate_bevel("exp",bevel_end = 0.4),
max_height = 3000, scale_all_max = TRUE, set_max_height = TRUE,
material = rayvertex::material_list(diffuse="red",
ambient = "darkred",
diffuse_intensity = 0.2,
ambient_intensity = 0.1),
light_intensity = 1, light_relative = FALSE,
extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), bevel_height = 5000,
base_height=0, clear_previous = TRUE,
zscale=200)
render_snapshot()
}
#> Warning: st_centroid assumes attributes are constant over geometries
#> Warning: st_centroid does not give correct centroids for longitude/latitude data
# While the bevels all start at the same point in the above example,
# they rise to different levels due to being scaled by the maximum internal distance
# in the polygon. Setting `scale_all_max = TRUE` ensures the bevels are all scaled to the
# same maximum height (in this case, 3000m above the 5000m bevel start height).
if(run_documentation()) {
render_beveled_polygons(mont_county_buff, flat_shading = TRUE, heightmap = montereybay,
bevel = raybevel::generate_bevel("exp",bevel_end = 0.4),
max_height = 3000, scale_all_max = TRUE, set_max_height = TRUE,
material = rayvertex::material_list(diffuse="red",
ambient = "darkred",
diffuse_intensity = 0.2,
ambient_intensity = 0.1),
light_intensity = 1, light_relative = FALSE,
extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), bevel_height = 5000,
base_height=0, clear_previous = TRUE,
zscale=200)
render_snapshot()
}
#> Warning: st_centroid assumes attributes are constant over geometries
#> Warning: st_centroid does not give correct centroids for longitude/latitude data
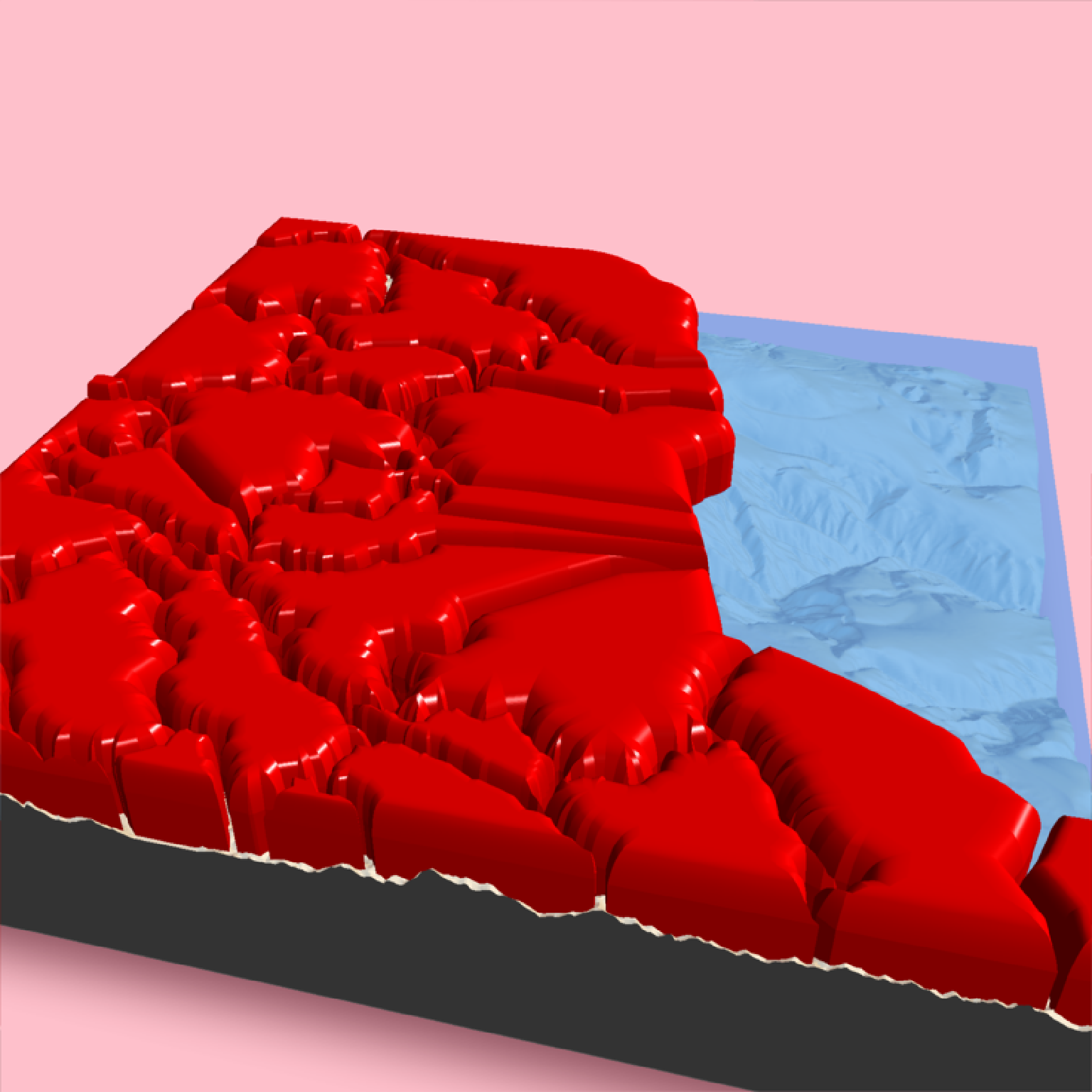 # Rendering the polygons with `render_highquality()`
if(run_documentation()) {
render_highquality()
}
# Rendering the polygons with `render_highquality()`
if(run_documentation()) {
render_highquality()
}
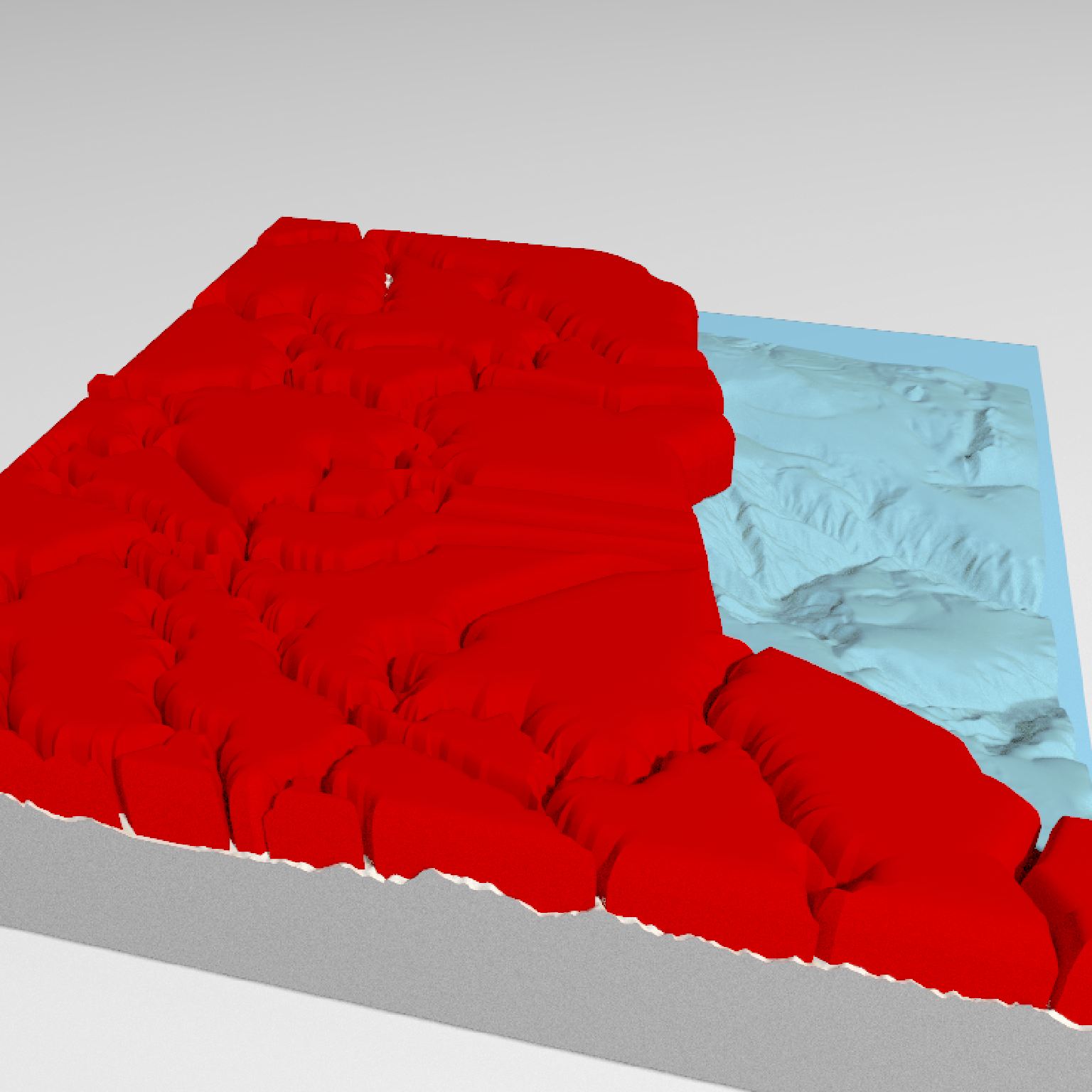 # We can scale the size of the polygon to a column in the `sf` object as well:
# raybevel::generate_bevel() function. We can scale this data down using the `scale_data`
# argument. Note that this is applied as well as the `zscale` argument, and that you
# must think carefully about your scales and values if trying to represent a meaningful
# data visualization with this object.
if(run_documentation()) {
render_beveled_polygons(mont_county_buff, flat_shading = TRUE, angle = 45, bevel_width=1000,
data_column_top = "ALAND", scale_data = 1e-5, heightmap = montereybay,
#max_height = 1000, scale_all_max = TRUE, set_max_height = TRUE,
material = rayvertex::material_list(diffuse="red"),
light_intensity = 1, light_relative = FALSE,
extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), clear_previous = TRUE,
zscale=200)
render_snapshot()
}
#> Warning: st_centroid assumes attributes are constant over geometries
#> Warning: st_centroid does not give correct centroids for longitude/latitude data
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 4.704823, calculating full polygon model
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 0.720301, calculating full polygon model
# We can scale the size of the polygon to a column in the `sf` object as well:
# raybevel::generate_bevel() function. We can scale this data down using the `scale_data`
# argument. Note that this is applied as well as the `zscale` argument, and that you
# must think carefully about your scales and values if trying to represent a meaningful
# data visualization with this object.
if(run_documentation()) {
render_beveled_polygons(mont_county_buff, flat_shading = TRUE, angle = 45, bevel_width=1000,
data_column_top = "ALAND", scale_data = 1e-5, heightmap = montereybay,
#max_height = 1000, scale_all_max = TRUE, set_max_height = TRUE,
material = rayvertex::material_list(diffuse="red"),
light_intensity = 1, light_relative = FALSE,
extent = attr(montereybay,"extent"), clear_previous = TRUE,
zscale=200)
render_snapshot()
}
#> Warning: st_centroid assumes attributes are constant over geometries
#> Warning: st_centroid does not give correct centroids for longitude/latitude data
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 4.704823, calculating full polygon model
#> All `bevel_offset` greater than max offset in polygon of 0.720301, calculating full polygon model